Get in touch to find a permanent solution for your well
Businesses worldwide are benefitting from BiSN's well services in the field. Contact us today and embrace tomorrow's downhole well solution, today.
Well Abandonment with Wel-lok™ STC


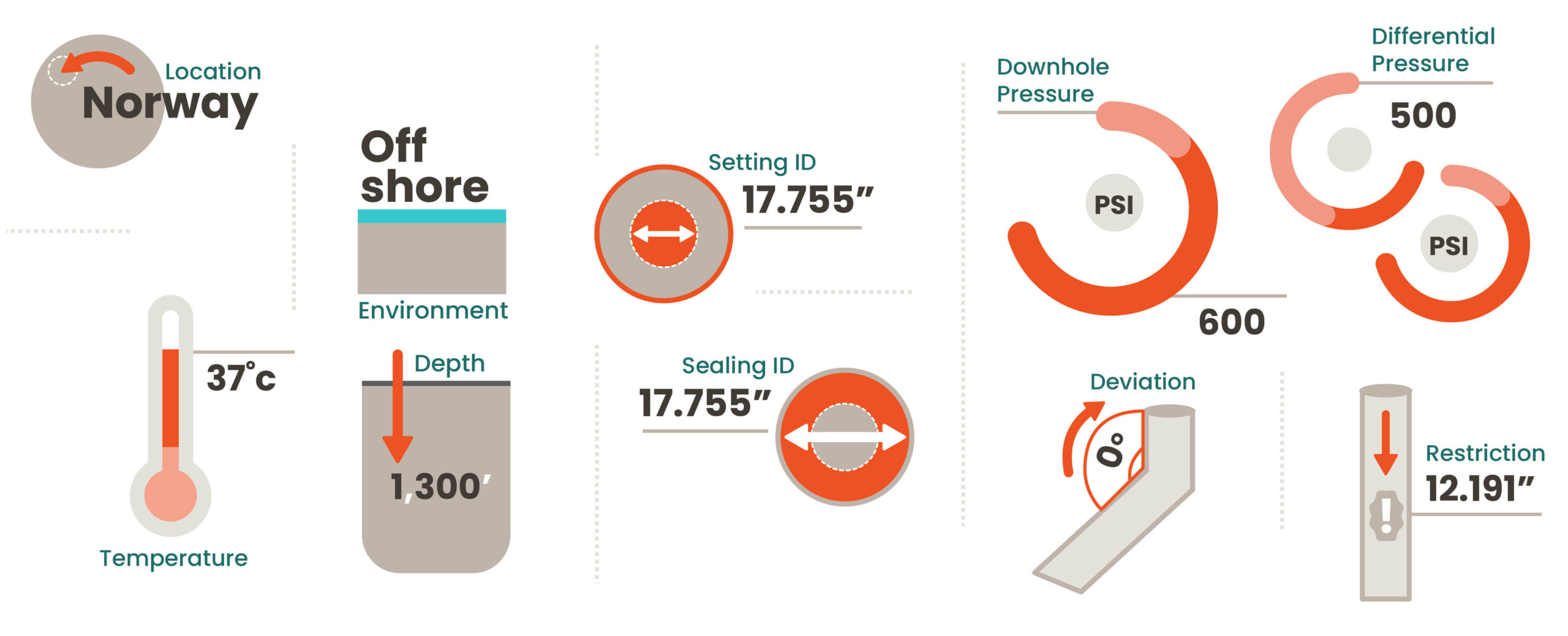
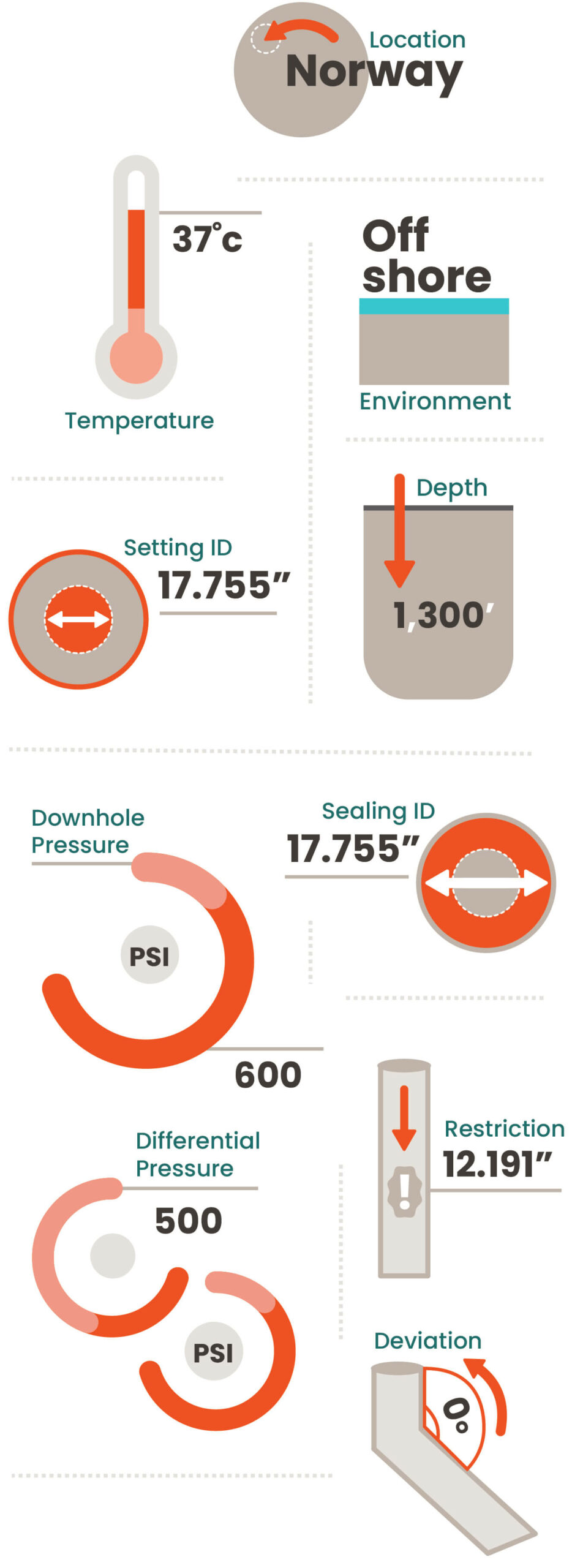
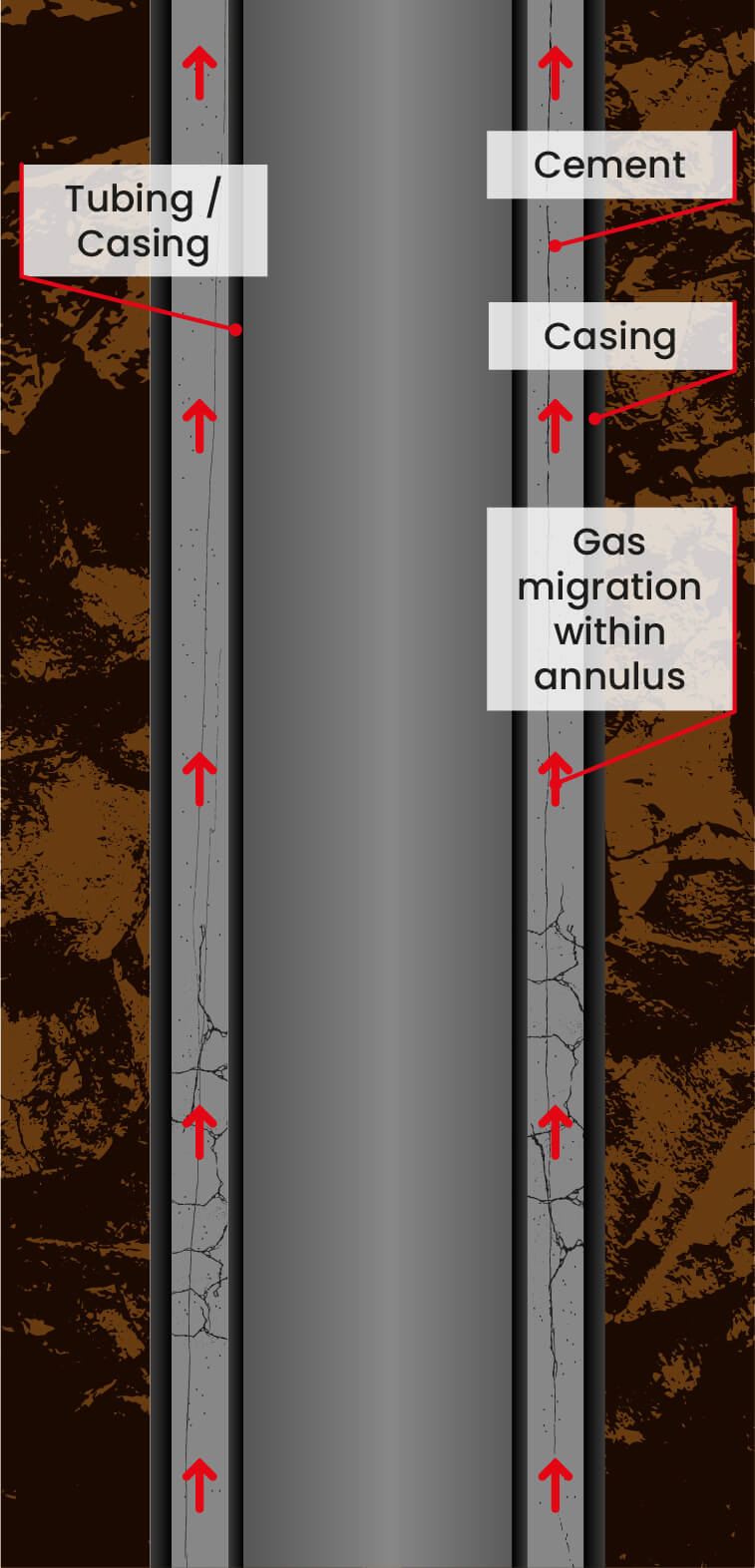
Traditional well abandonment includes placing a surface cement plug through a section milled window or by perforating and washing out existing cement. While cement is widely recognized as the standard abandonment material throughout the world, its ability to block gas in a well is lacking because it is a porous material that shrinks when it solidifies. To reduce environmental risk, and operator’s long-term liability, a new abandonment material is needed to ensure a well is properly capped during well abandonment operations.
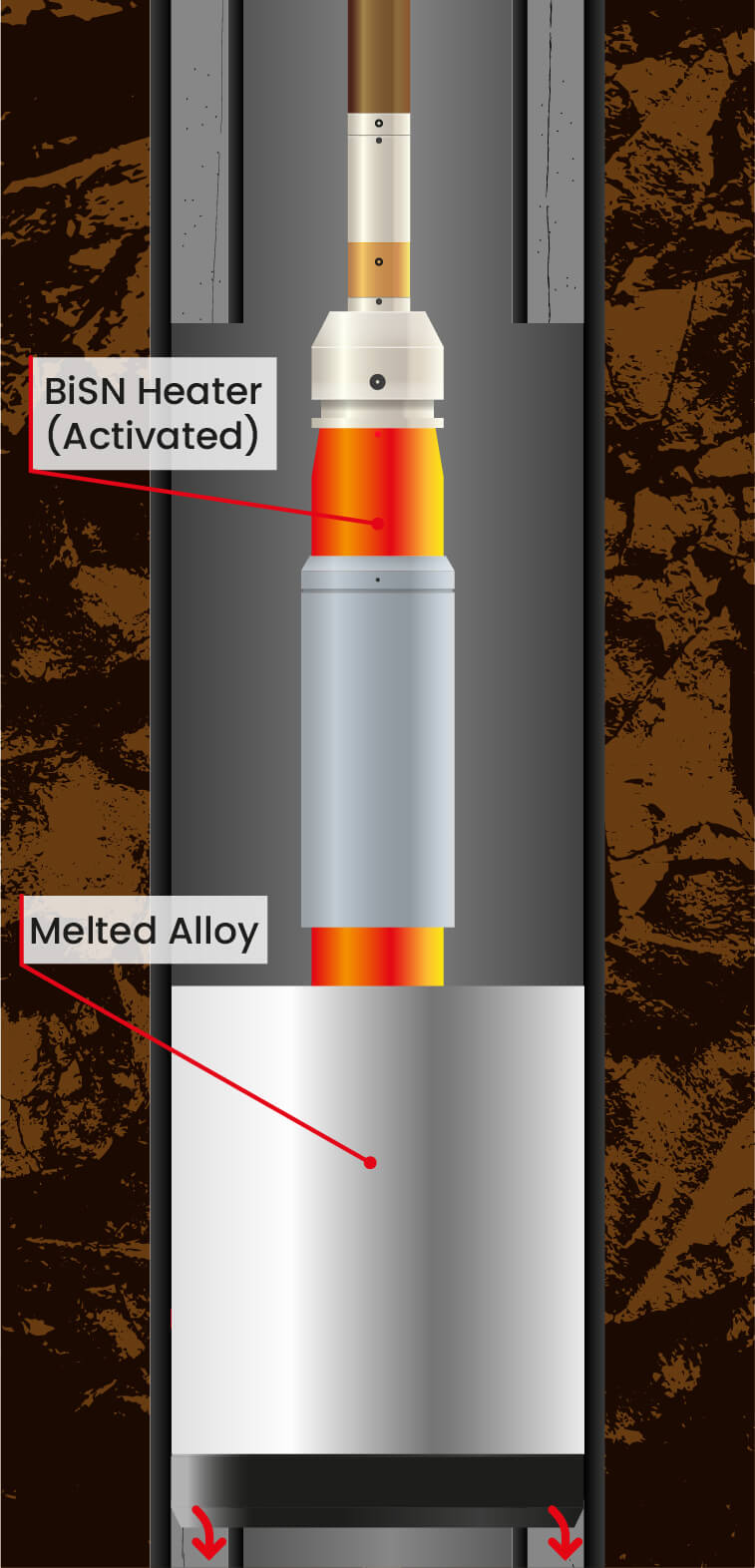
Surface plugs are set in the outermost casings which are relatively large, requiring a large volume of material to seal. This was the largest tool BiSN had ever run with over 3,500 kg of bismuth alloy to seal out to 18 5/8” casing. Due to abandonment regulations, a single material plug was required across the wellbore. To achieve this, the modified thermite heater used to melt the alloy would need to be removed while the alloy was still liquid. This was also a first for BiSN.
BiSN deployed the largest ever bismuth alloy plug, a Wel-lok™ STC to seal through a section milled window in 13 3/8’ casing out to 18 5/8” casing.
Prior to running the Wel-lok™ STC, a window was section milled in the 13 3/8’ casing out to the 18 5/8” casing and the client perforated a shallow gas zone to ensure the plug would have gas and differential pressure from below in order to verify the seal. Live and memory gauges were hung in the well for long term monitoring below the STC. After running to the desired depth on electric line, the modified thermite heater was activated melting the bismuth alloy. After 35 minutes, a time pre-determined during the 1 ½” year qualification testing program, the heater was pulled from the alloy, leaving a single material barrier in across the wellbore out to the 18 5/8” casing. This seal is now under a 2-year monitoring plan and no bubbles or pressure have been observed above the plug since it was set.
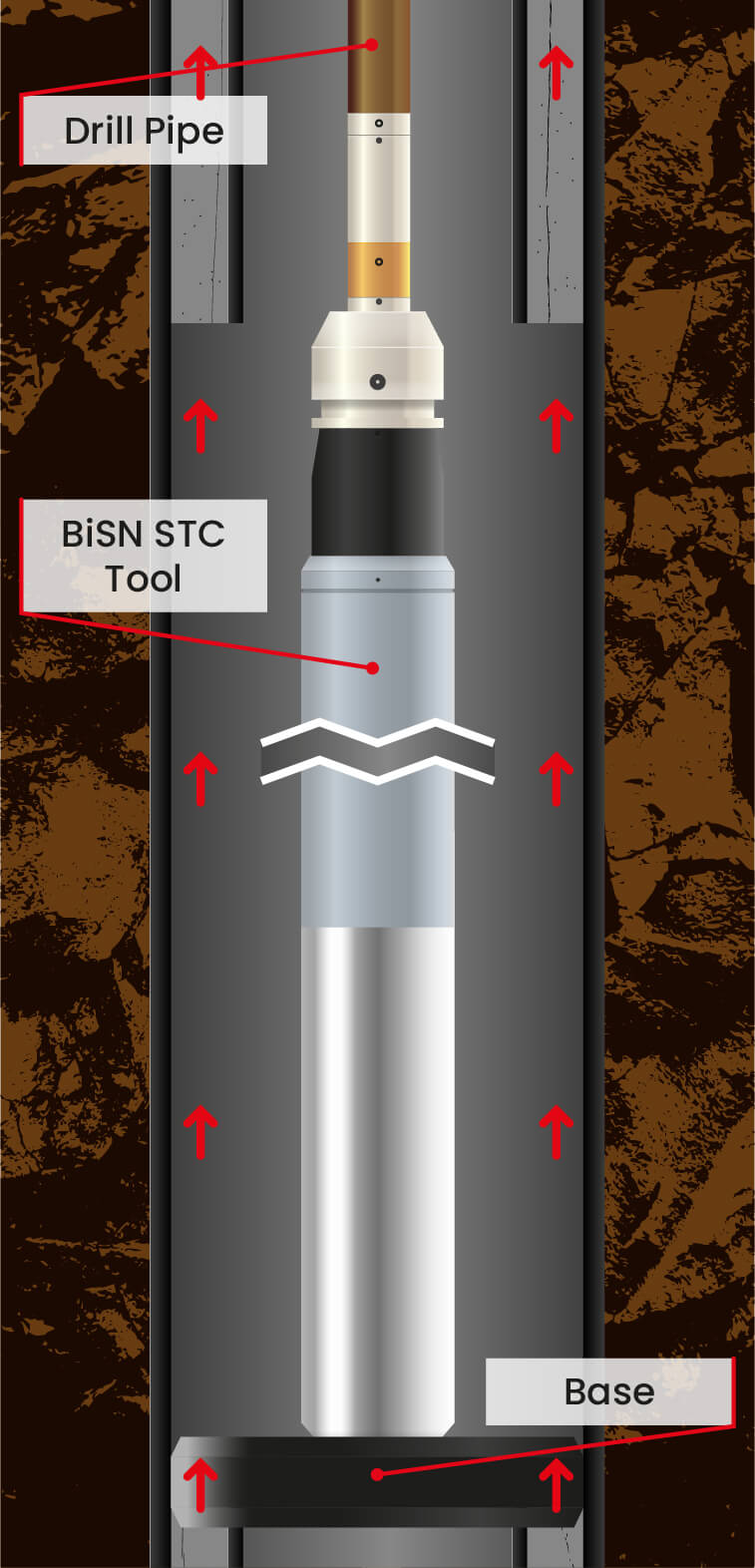
The Wel-lok™ STC (Seal Through Casing) has been developed to achieve a gas tight V0 seal well annuli that cannot be achieved by traditional cement balance plugs. Run on electric line, this tool does not need surface pumping equipment to circulate the alloy in place. Due to its viscosity and density, once melted the liquid alloy will flow with gravity into the annulus. When it cools below its melting point it solidifies, expands and creates a gas tight seal across the entire wellbore. The entire process, from melting to solidification, takes place in minutes and the seal is ready to test within an hour.




Businesses worldwide are benefitting from BiSN's well services in the field. Contact us today and embrace tomorrow's downhole well solution, today.
Our website uses analytics, marketing and preference cookies to both provide the most relevant experience for our users and to give us information about how our site is used. By clicking “Accept All”, you consent to the use of these cookies. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide a controlled consent.
Accept All Cookies